New Book: Information Security and Privacy in the Digital World – Some Selected Topics, Intech Open.
Editors: Jaydip Sen, Praxis Business School, India, and Joceli Mayer, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Brazil.
Abstract – In the era of generative artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) and while there is explosive growth in the volume of data and the associated need for processing, analysis, and storage, several new challenges have arisen in identifying spurious and fake information and protecting the privacy of sensitive data. This has led to an increasing demand for more robust and resilient schemes for authentication, integrity protection, encryption, non-repudiation, and privacy preservation of data. This book presents some of the state-of-the-art research in the field of cryptography and security in computing and communications. It is a useful resource for researchers, engineers, practitioners, and graduate and doctoral students in the field of cryptography, network security, data privacy issues, and machine learning applications in the security and privacy in the context of the IoT.
Joceli Mayer
Blog on Digital Signal Processing
A New Chapter Published
“Review on Watermarking Techniques Aiming Authentication of Digital Image Artistic Works Minted as NFTs into Blockchains”, by Joceli Mayer. To appear in the book “Information Security and Privacy in the Digital World – Some Selected Topics”, edited by Prof. Jaydip Sen and Prof. Joceli Mayer, IntechOpen, DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.107715, Oct, 2022.
Review on Watermarking Techniques Aiming Authentication of Digital Image Artistic Works Minted as NFTs into Blockchains, Joceli Mayer
Chapter will appear in the book, “Information Security and Privacy in the Digital World –
Some Selected Topics”
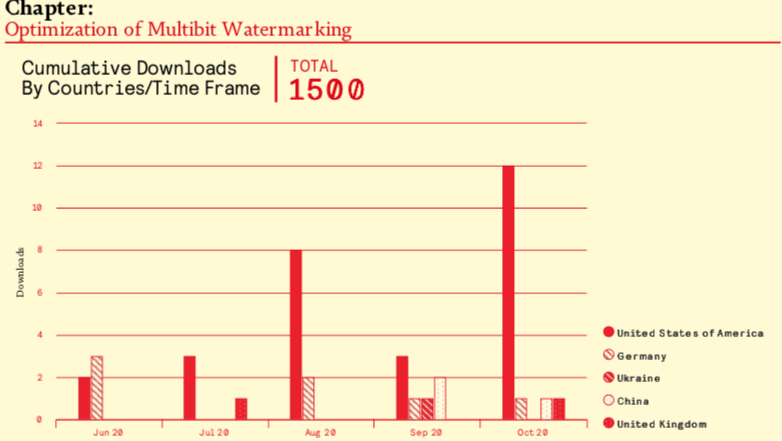
Chapter Book “Optimization of Multibit Watermarking” Achieved 1500 Downloads
O Profissional do Futuro
Nessa Ted Talk Michelle fala sobre o profissional do futuro. Ela aborda a evolução do mercado de trabalho nos últimos anos e as mudanças que a tecnologia trouxe e ainda vai trazer nos próximos anos. Em um futuro em que as máquinas irão substituir metade da força global de trabalho, como os profissionais vão conseguir se diferenciar das máquinas e permanecerem humanos dentro de um mundo tão digital. Michelle é publicitária, dj, maratonista e atua hoje como Head de Educação no LinkedIn Brasil. Apaixonada por tecnologia, depois de algumas viagens para o Vale do Silicio onde visitou as universidades mais inovadoras de lá, acabou se apaixonando também pelo mundo da Educação.
This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community. Learn more at https://www.ted.com/tedx.
Fundamentals and Applications of Hardcopy Communication: Conveying Side Information by Printed Media, by Joceli Mayer, Paulo V. K. Borges, Steven J. Simske. Springer, 2018.

This book presents covert, semi-covert and overt techniques for communication over printed media by modifying images, texts or barcodes within the document. Basic and advanced techniques are discussed aimed to modulate information into images, texts and barcodes.
Conveying information over printed media can be useful for content authentication, author copyright, information and piracy product deterrent, side information for marketing, among other applications.
Practical issues are discussed and experiments are provided to evaluate competitive approaches for hard-copy communication.
This book is a useful resource for researchers, practitioners and graduate students in the field of hard-copy communication by providing the fundamentals, basic and advanced techniques as examples of approaches to address the hard-copy media distortions and particularities.
News: AI is changing the way medical technicians work
From: by Tristan Greene — 1 day ago in Artificial Intelligence
When MIT successfully created AI that can diagnose skin cancer it was a massive step in the right direction for medical science. A neural-network can process huge amounts of data. More data means better research, more accurate diagnosis, and the potential to save lives by the thousands or millions.
In the future medical technicians will become data-scientists to support the AI-powered diagnostics departments that every hospital will need. Radiologists are going to need a different education than the one they have now — they’re gonna need help from Silicon Valley.
This isn’t a knock against radiologists or other medical technicians. For ages now, they’ve worked hand-in-hand with doctors and been crucial in the diagnostic process. It’s just that machines can process more data, with greater efficiency, than any human could. For what it’s worth, we’ve predicted that doctors are on their way out too, but this is different.
Geoffrey Hinton, a computer scientist at The University of Toronto, told the New Yorker:
I think that if you work as a radiologist you are like Wile E. Coyote in the cartoon. You’re already over the edge of the cliff, but you haven’t yet looked down. There’s no ground underneath. It’s just completely obvious that in five years deep learning is going to do better than radiologists. It might be ten years.
It’s not about replacing, but upgrading and augmenting. Hinton might be a little dramatic, but not for nothing: he’s the grandson of famed mathematician George Boole, the person responsible for boolean algorithms. Obviously, he understands what AI means for research. He’s not suggesting, however, that radiologists don’t do anything beyond pointing out anomalies in pictures.
Instead, he’s intimating that traditional radiology is going to change, and the way we train people now is going to be irrelevant. Which is, again, harsh.
Nobody is saying that medical trainers and educational facilities are doing a bad job. It’s just that they need to be replaced with something better. Like machines.
We don’t have to give neural-networks the keys to the shop; we’re not creating autonomous doctor-bots that’ll decide to perform surgery on their own without the need for nurses, technicians, or other staff. Instead we’re streamlining things that humans simply can’t do, like process millions of pieces of data at a time.
Tomorrow’s radiologist isn’t a person who interprets the shadows on an X-ray. They are data-scientists. Medical technicians are going to be at the cutting-edge of AI technology in the near future. Technology and medicine are necessary companions. If we’re going to continue progress in medicine, we need a forward-thinking scientific attitude that isn’t afraid of implementing AI.
Nowhere else is the potential to save lives greater than in medical research and diagnostics. What AI brings to the table is worth revolutionizing the industry and shaking it up for good. Some might say it’s long overdue.
Book on Image Enhancement and Coding
Blending Models for Image Enhancement and Coding:
Surface representation with polynomial blending functions for enhancement and coding of images and VRML models, Joceli Mayer, LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, december, 2015.
Link to Book
Recent Applied Research on Digital Signal Processing
Besides working with speech recognition and assistive technology, lately I have been working with some other research and applications of Digital Signal Processing theory:
On Informed Coding and Host Rejection for Communication over Inkjet Print-and-Scan Channels
Joceli Mayer and Steven J. Simske
This paper describes novel approaches to achieve robust communication over inkjet print-and-scan (IPS) color channels. The IPS color channel poses even greater challenges than the laser printer-and-scan channel due to the resulting mixing and spreading of the ink dots. We propose a novel informed coding and two host color rejection approaches, one based on a novel color rejection and another on a whitening filter, to deal with the aforementioned inkjet printer distortions. A substitutive spatial domain embedding is proposed to enable robustness optimization using the proposed informed coding. Analyses and examples are provided to evaluate the performance enhancement on robustness and transparency achievable by the proposed approaches.
Increasing the capacity of color print codes for robust communication over inkjet print-scan channels
Joceli Mayer
This investigation on robust and high capacity print codes aims to increase information payload in a given printed page area while providing robustness to channel errors including distortions originated by the inkjet printing and scanning processes. The approach includes statistical print-and-scan channel characterization, designing of robust segmentation using visual cues, unsupervised Bayesian color classification with expectation-maximization algorithm for parameters estimation of a mixture of Gaussians model and design of error correction codes. Results illustrate the performance evaluated under real channel and distortions conditions. High payload of 4592 bytes per squared inch is achieved with a robustness of 92\% to distortions due to the print-and-scan channel. Adding high-density information to printed materials enables interesting hardcopy document applications involving security, authentication, physical-electronic round tripping, item-level tagging, and consumer/product interaction.
Method for Correction of Lenses Distortion in Stereo Vision
Joceli Mayer and Osmando Pereira Junior
Lenses distortion is one of the main factors that limits the accuracy of stereo vision system reconstruction. We propose a new method for correction of the lenses distortion by applying compensation to each region of an image. Our method splits the image into smaller regions and compensates for each region for a fixed lenses model order. When compared to the conventional method, which models the entire image with only one model, our approach provides considerably better compensation and reduce the depth error as shown in the experiments with synthetic data.
Continuous Gesture Recognition using Hidden Markov Models
Joceli Mayer and Vinicius Breda
This work presents an algorithm for recognizing gestures in videos where the actions are executed continuously without pause between them and can be performed with one or both hands. We employ Hidden Markov Models (HMM) for modeling gestures as this technique has been applied successfully in speech and character recognition, We investigate the performance for a set of 26 visual descriptors extracted from the hands after a region segmentation based on normalized quadrants. Recognition are performed by adapting the Hidden Markov Models Toolkit (HTK) and achieve a recognition rate of 91.28% for a set of 21 phrases each composed of 4 gestures from a dictionary of 15 gestures from the Brazilian sign language (LIBRAS).
Informed communication system designed to embed hidden information into audio advertisements
Joceli Mayer and Luiz F.L.O. Silva
Investigation on informed communication system designed to embed hidden information into audio advertisements. The information is modulated and transmitted through a audio digital watermark embedded into the audio signal host. The watermark embedding is designed to achieve minimal perceptual impact and high robustness to environment distortions in order to comply with the proposed application in marketing. The embedding energy is properly scaled in order to achieve high transparency. Novel synchronization and adaptive equalization techniques are investigated and proposed to reliably extract the information after the channel interferences. Experimental results using simulated and real environment channels illustrate the performance of the proposed system and results are contrasted to other existing techniques.